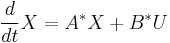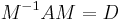Modal matrix
In linear algebra, the modal matrix is used in the diagonalization process involving eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
Assume a linear system of the following form:
where X is n×1, A is n×n, and B is n×1. X typically represents the state vector, and U the system input.
Specifically the modal matrix M is the n×n matrix formed with the eigenvectors of A as columns in M. It is utilized in
where D is an n×n diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues of A on the main diagonal of D and zeros elsewhere. (note the eigenvalues should appear left→right top→bottom in the same order as its eigenvectors are arranged left→right into M)
This process is also known as the similarity transform.